UC14 - CardioWheel
As a key element of the driving task and road safety, it is of extreme importance to guarantee that the driver (or tele-operator) of a vehicle is in cognitive state complacent with the skill, readiness,and responsibility such task demands. Moreover, in some specific contexts, such as professional fleet and share-driving vehicles, it is essential to verify the identity of the driver, ensuring correct liability in case of accidents, vehicle misuse, and digitalization of the process.
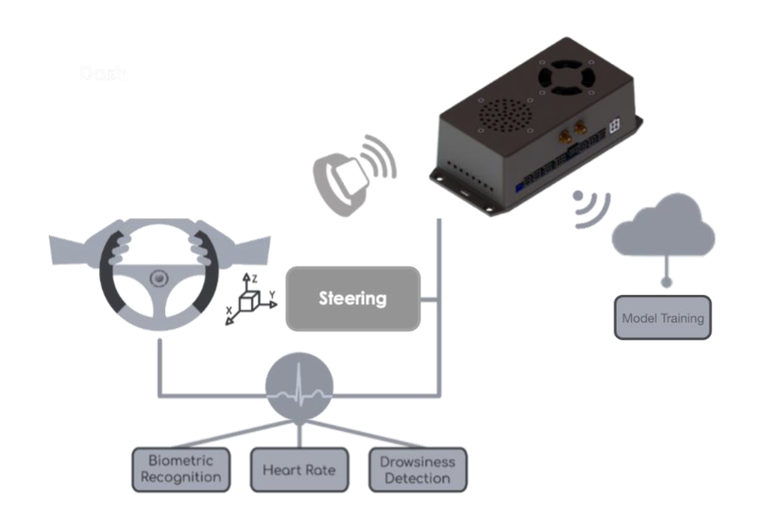
CardioWheel is an Advanced Driver Assistance System that acquires ECG (electrocardiogram) from the driver’s hands to continuously detect drowsiness, cardiac health problems, and perform biometric identity recognition [3][4]. It(see Figure 1)is composed of an analog front-end, which measures the ECG signal, and an embedded processing unit that performs signal processing and sends information to the CardioGW using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). ECG measurement uses two dry electrodes, seamlessly integrated into a steering wheel cover, using conductive materials. This system is protected under patent WO2013109154A1.

To enable real-time ECG-based driver monitoring, the CardioWheel is inserted into an ecosystem, consisting of the device itself, a gateway (CardioGW)that communicates with CardioWheel via BLE to collect the ECG data and a cloud service where machine learning models are trained before being installed in the CardioGW, see Figure 2. The system is based on pre-trained models that were fitted using larger curated datasets, but that are refined using data collect from drivers using the system. GDPR compliance is guaranteed by the design of the system.
CardioWheel
CardioWheel is an off-the-person single lead ECG recording device. It is dimensioned to acquire ECG signal from two dry electrodes made of conductive leather. The front-end of the system performs signal filtering, conditioning,and digitalization, as well as detectionof contact with the steering wheel. Sampled at fixed sampling rate these signals, ECG and LOD (Lead On Detection) are sent via BLE to the CardioGW.
CardioGW
The CardioGW is an information aggregation platform powered by a single board computer. It is responsible for receiving the data stream from CardioWheel and performing digital filtering, feature computing and classification of that data for the different tasks: Identification, drowsiness detection, distraction detection, etc.
The code base used for all these tasks is pre-installed on the single board computer, however, features are sent to the cloud service to train the model instances to be used later on local classification tasks, with trained models being returned and stored in the CardioGW.
Cloud
Given the intense computational requirements for cost function optimization in machine learning model training, these tasks are not performed locally but instead rely on a cloud server that can complete them more quickly and safely within system specifications.The cloud server receivescyphered data corresponding to the feature set with which it trains a specific instance of a classifier. The trained classifier is then transmitted to the corresponding CardioGW, where it is stored and evaluated locally.
Being an ADA system that has no direct intervention on the vehicle behavior, but instead works as a warning system, CardioWheel’s safety violations do not result in immediate harm to its user. Because of that, in this use case, safety violations are thought of as situations where requirement breach leads to a misinformed driver and so, a potentially dangerous one. As an example, if the system were to incorrectly classify a driver as being alert when, in reality, he was already drowsy, the incorrect assessment of his state could bolster a false sense of security that potentially leads to a traffic accident. Following the same principle, system requirements, on which correct signal processing and interpretation are dependent, are considered to be safety related ones.
